Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the intricate world of welding.
Today, we’re exploring a crucial aspect of welding qualifications – the 2G welder certification. You may be wondering what this entails and why it holds such significance.
Well, allow us to simplify it for you. The 2G welder qualification is a credential that validates an individual’s expertise in welding in a vertical position using a groove joint.
So put on your helmet and join us as we take a closer look at the qualifications of a 2G welder.
What is 2G Welding Position
Contents
Curious about the enigmatic world of 2G welding position and its nuances? As a seasoned welding expert, I am here to demystify this fundamental welding position for you. So, let’s plunge into the depths of knowledge and unravel all the secrets surrounding it.
What Exactly is 2G Welding Position?
2G welding position is a horizontal stance where the weld axis is parallel to the ground, while the pipe is held vertically. The welder operates from the side of the pipe, with the workpiece aligned parallel to their body. This position is primarily used for joining thin sheets and plates at a 90-degree angle.
The Origin of “2G”
The term “2G” stands for “2nd generation,” representing its placement in a series of four fundamental welding positions (1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G). Each position signifies a distinct orientation of the weld axis and workpiece, with 1G being the simplest and 4G being the most challenging.
How is it Tested?
The quality of welds produced in the 2G position is critical, which is why they undergo rigorous testing to meet specific standards set by regulatory bodies such as AWS or IIW. These tests evaluate a welder’s proficiency in creating robust, long-lasting, and flawless welds.
The Advantages of Acquiring a 2G Welder Qualification
Acquiring a 2G welder qualification can unlock various opportunities for welders in diverse industries like construction, manufacturing, and oil and gas. It not only showcases their technical expertise but also their understanding of welding codes and procedures, making them invaluable assets to any organization.
Where Do You Use 2G Welding
Have you ever pondered upon the uses of 2G welding and its significance in the welding world? As a master welder with years of expertise, I have personally witnessed the flexibility and effectiveness of this technique, making it a fundamental skill in various industries.
Let’s begin with the basics. 2G welding is a horizontal position where the welder moves around the welded joint while applying the weld. It is a widely used method in construction, manufacturing, automotive, shipbuilding, aerospace, and oil and gas industries.
In construction, 2G welding plays a vital role in structural steel works like building frames, bridges, and pipelines. The horizontal position allows easy access to weld joints commonly found in these projects. What sets 2G welding apart is its ability to create robust and long-lasting welds that can withstand heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions.
The manufacturing sector also heavily relies on 2G welding for fabricating metal parts and components. The horizontal position enables precise control and accuracy when welding smaller, intricate metal pieces. This makes it a top choice for manufacturers who require consistent and high-quality welds for their products.
In the automotive industry, 2G welding is essential for welding various vehicle components like frames, exhaust systems, and body panels. Once again, the horizontal position proves beneficial in accessing tight spaces and creating strong welds for repairing or replacing damaged parts on vehicles.
But its usage is not confined to these industries alone; 2G welding finds its place in shipbuilding, aerospace, and oil and gas sectors as well. In shipbuilding, it plays a crucial role in creating sturdy welds on large metal structures such as ships and offshore platforms. The aerospace industry utilizes 2G welding to fabricate precise aircraft components that require meticulous attention.
Characteristics Of The 2G Welding Position
Mastering the 2G welding position is a vital skill for any welder striving to excel in their trade. This versatile technique is widely used in various industries, making it a must-have in any welder’s repertoire. In this segment, we will delve deeper into the characteristics of the 2G welding position and how to attain perfection in this method.
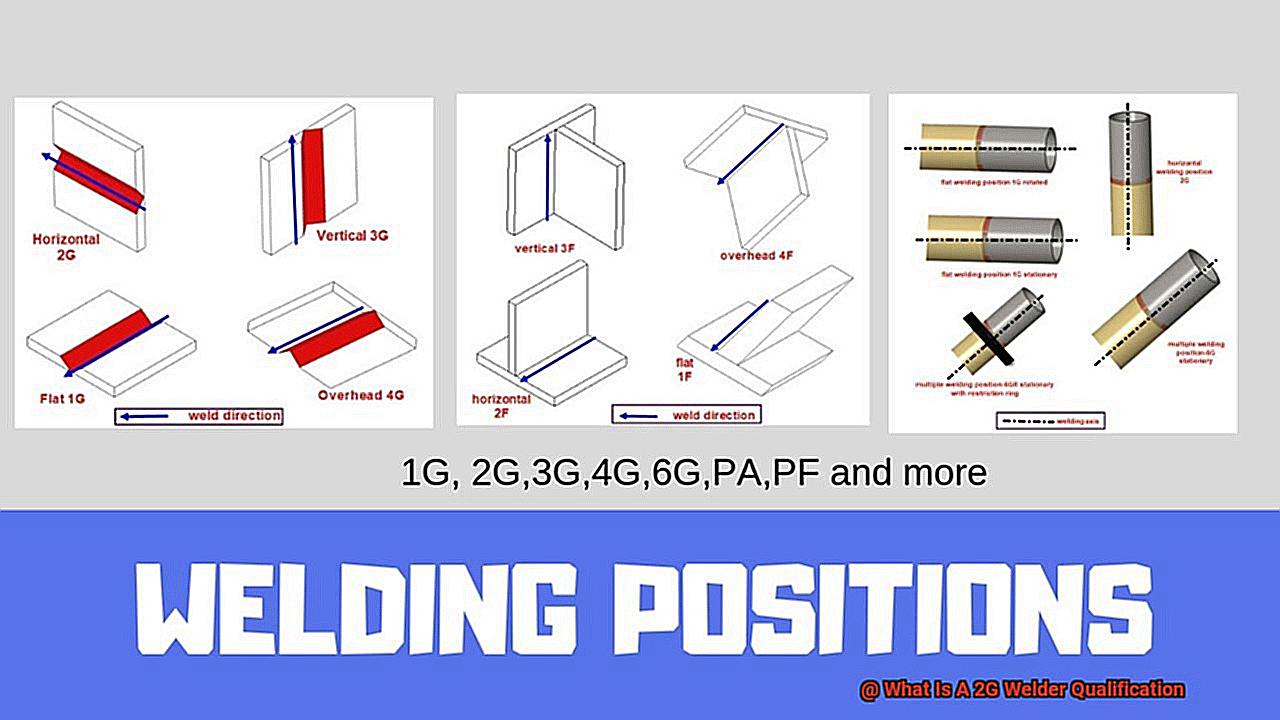
Horizontal welding is the primary approach used in the 2G welding position. It involves welding grooves on flat or horizontal surfaces, making it ideal for pipe welding. This technique requires precision and expertise, as any uneven distribution of weld metal can lead to weak and unstable joints. To achieve an even distribution of weld metal, it is imperative to maintain a consistent travel speed and electrode angle throughout the welding process.
One of the key benefits of the 2G welding position is its perfect application for flat or horizontal surfaces. Welding on a level surface allows gravity to assist in shaping the weld pool, resulting in stronger and more stable joints. This position is also suitable for welding thin sheet metal and plates, where precision and control are crucial.
Another variation of the G welding position is the G pipe welding position. In this technique, the pipe is positioned vertically, and welding is performed on the side surface in a horizontal direction. This method requires a high level of skill and control as the welder must maintain a consistent arc length while moving along the circumference of the pipe.
To become an expert in the G welding position, regular practice and continuous improvement are crucial. It is also helpful to have a comprehensive understanding of different types of electrodes, their properties, and how they affect your welding technique.
In conclusion, mastering the 2G welding position is essential for any welder looking to elevate their craft. Its versatility makes it an invaluable skill across various industries, from pipe welding to fabrication. With consistent practice and dedication to improvement, you can become a master at the G welding position and take your welding skills to new heights.
What is the Qualification Range for 2G
The range of qualifications for the 2G welding position is a critical aspect of becoming a proficient welder. This intricate technique, utilized in various fields, demands precision and expertise to achieve impeccable results. But what exactly does it entail to be qualified in 2G? Let’s delve deeper into the qualification spectrum for this position and explore the potential it presents for welders.
Positions Available for 2G Certification
As per the standards set by the American Welding Society (AWS), a welder with G qualification can only perform welding in horizontal (G) and flat (G) positions. However, if a welder has G, G, and G qualifications, they are deemed proficient in all positions. This means that with additional certifications, welders can expand their knowledge and take on more intricate welding tasks.
Impact of Different Positions on Qualifications
The G position refers to pipe welding, where the pipe axis is vertical or near-vertical, and the pipe rotates during the process. This position requires specialized skills and knowledge of electrode properties to ensure adequate penetration and fusion. In contrast, the G position involves flat welding on a horizontal surface. Welders must possess a steady hand and precise control of the electrode to achieve top-notch results in this position.
Opportunities for 2G Certified Welders
With a 2G certification, welders can undertake various welding projects such as constructing structures, pipelines, and pressure vessels. These opportunities are not confined to a particular industry, making it a versatile skillset that can lead to job opportunities in sectors like construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding.
According to AWS D., a 2G certification also enables welders to work on pipes or tubing over 24 inches (600 mm) in diameter or plates for the positions they are qualified in. This opens up even more doors for welders to progress in their careers and tackle challenging projects.
Pros
The field of welding is in a constant state of evolution, requiring skilled professionals who can handle intricate tasks with precision and mastery. As a welder, obtaining a 2G welder qualification can open up a plethora of opportunities for career growth and personal development. In this article, we will delve into the advantages of having a 2G welder qualification and how it can elevate your performance in the welding industry.
But what exactly does a 2G welder qualification entail? This certification is specifically designed to assess an individual’s proficiency in welding various materials using different techniques, such as SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) or GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding). It is one of the most coveted qualifications in the welding industry, recognized globally for its standards.
One of the greatest benefits of obtaining a 2G welder qualification is the potential for career progression. Many companies require their employees to possess this certification before considering them for higher positions. Not only does this showcase your expertise in welding, but it also highlights your dedication to continuous learning and improvement, setting you apart from other candidates in the eyes of employers.
Moreover, a 2G welder qualification offers versatility in the type of work you can undertake. With this certification, you can work with a variety of materials and industries, including construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding. This adaptability makes 2G welders highly sought-after, ensuring job security even during uncertain economic times.
An additional benefit of having a 2G welder qualification is the assurance of delivering quality work. This certification attests that you have been trained and evaluated on specific welding techniques, meeting industry standards. Companies are more likely to hire individuals with this qualification as it guarantees that they will produce top-notch work and minimizes the risk of errors or accidents on the job.
Moreover, obtaining a 2G welder qualification can lead to greater earning potential.
Cons
In any line of work, there are always two sides to the coin. While obtaining a 2G welder qualification may seem like a wise decision, it is crucial to weigh the potential cons before diving in headfirst. As experienced welders, we aim to provide a comprehensive perspective on this matter.
Restricted Job Opportunities:
One of the major drawbacks of pursuing a 2G welder qualification is the limited job opportunities available. As a 2G welder, your skills will be limited to fillet welding in flat and horizontal positions. This could hinder your chances of securing jobs in industries that require welders with versatile qualifications, putting you at a disadvantage in the job market.
Lower Earning Potential:
Another possible downside of pursuing a 2G welder qualification is the lower earning potential compared to higher-level certifications. Due to the specialized nature of 2G welding and the limited job opportunities, employers may not offer as high of a salary for this type of work. This could result in slower career growth and fewer chances for advancement compared to those with higher qualifications who can perform more complex welds.
Physical Demands:
It is no secret that welding is a physically demanding job, and obtaining a 2G welder qualification does not exempt you from this fact. In fact, fillet welding in flat and horizontal positions requires more physical exertion as it involves working at different angles and positions. This can lead to strain and fatigue on the body, increasing the risk of injuries such as burns or strains. Aspiring 2G welders should be aware of these physical demands and take necessary precautions to prevent potential injuries.
2G vs 2F Welding Positions
The realm of welding is a vast and intricate one, with an array of positions and techniques to be mastered. As experts in the field, we are often asked the question, “What differentiates 2G from 2F welding positions?” While both positions involve the joining of two metal pieces, there are significant distinctions that every aspiring welder must comprehend.
Let’s begin with the fundamentals. In F welding, the weld takes on a triangular shape between two surfaces that are perpendicular to each other. This type of weld is commonly known as a fillet weld. On the contrary, G welding involves creating a groove joint, where the weld’s face is in a vertical plane. This means that in F welding, the welder works on the upper side of the horizontal and vertical surfaces, while in G welding, they work on a vertical plane with the weld’s face lying on it.
But why does this matter? Well, for starters, it affects the shape of the weld. In F welding, the triangular shape distributes stress evenly, resulting in a stronger joint. On the other hand, G welding allows for deeper penetration and a more robust bond between the two metal pieces.
Another vital aspect to consider is the placement of the weld on metal surfaces. In F welding, the joint is situated at a right angle, making it easier for beginners to access and maneuver. Conversely, G welding requires working on a vertical plane, which can be more challenging and may cause sagging of the weld puddle.
As experienced welders, we understand that mastering G welding can be more perplexing than F welding. However, with perseverance and dedication, it can unlock a whole new world of job opportunities. Several industries, such as shipbuilding and construction, demand skilled individuals who can perform G welding on thicker materials.
Before delving into specialized training for 2G welding, there are some crucial factors to contemplate. Limited job opportunities and lower earning potential are some drawbacks that must be carefully weighed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 2G welder qualification is a vital certification for individuals looking to excel in the field of welding.
This qualification demonstrates proficiency in performing vertical welds using a groove joint, requiring precision, control, and specialized knowledge. With this qualification, doors to various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding can open up for career growth and advancement.
But with dedication and continuous improvement, one can become a master at the 2G welding position and elevate their skills to new heights.