Electricity is the lifeblood of modern society. It powers everything from our homes and workplaces to the factories that produce the goods we rely on. However, not all electricity is created equal. In fact, most of us receive three-phase power, which can be a bit of a challenge if we need to convert it to single-phase 220V, 240V or 120V.
But fear not. Converting from three-phase to single-phase power is easier than you might think. And with this blog post as your guide, you’ll have all the information you need to get the job done safely and efficiently.
First things first: let’s talk about what makes three-phase power different from single-phase power. We’ll cover the basics of electrical power and explain why three-phase power is so common in industrial and commercial settings.
Once you’ve got a good understanding of the differences between these two types of power, we’ll dive into various methods for converting three-phase power to single-phase power. Whether you’re using a phase converter, rewiring your system or using a transformer, we’ve got you covered.
Of course, safety is always a top priority when working with electricity. That’s why we’ll also provide some helpful tips on how to stay safe during the conversion process.
Whether you’re an experienced electrician or just someone looking to learn more about electrical systems and conversions, this blog post has something for everyone. So let’s get started.
What is 3-Phase Power?
Contents
The answer lies in 3-phase power – a type of electrical power that is utilized by three alternating currents with the same frequency and amplitude.
3-phase power is preferred over single-phase power in industrial and commercial settings because it is more efficient and cost-effective. In a 3-phase power system, the voltage between any two phases is 1.73 times the voltage of a single phase. This means that three-phase power can transmit more power using less copper wire than a single-phase system.
The three phases in a 3-phase power system are labeled A, B, and C, and the currents in each phase are separated by one-third of a cycle. This results in the sum of the currents in all three phases to be zero at any given moment, which helps to reduce the amount of ripple in the power supply. This improves the efficiency of electrical equipment that runs on 3-phase power, making it an ideal choice for industrial and commercial applications where high-power equipment is needed.
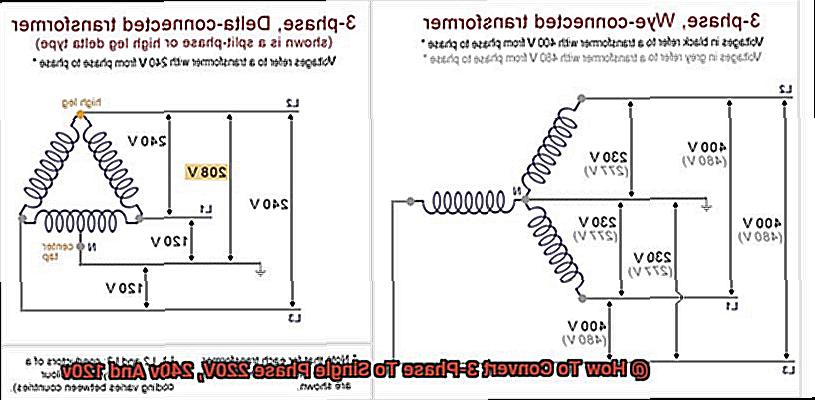
However, not all machines can run on 3-phase power – some require single-phase power to operate efficiently. To convert 3-phase power to single-phase power, a transformer with a delta-wye configuration can be used. This type of transformer has three primary windings connected in delta formation and three secondary windings connected in wye formation. The three-phase power is connected to the primary winding, and the single-phase output is taken from one of the secondary windings.
It’s important to note that converting 3-phase power to single-phase power results in a loss of power efficiency. Reducing the number of turns reduces the voltage output and increases the current required to operate devices at their rated power.
In conclusion, 3-phase power is an efficient method of transmitting electrical power, making it ideal for use in industrial and commercial applications where heavy machinery is needed. Understanding the basics of 3-phase power is an important first step in learning how to convert it to single-phase power for welding or other applications that require lower voltages.
What is Single-Phase Power?
Single-phase power is an integral component of the electrical grid that powers homes and small businesses worldwide. This type of power is characterized by a single waveform that oscillates at a specific frequency, typically 60 Hz in the United States. It can be delivered through a single wire or two wires that are 180 degrees out of phase with each other, making it flexible and versatile for various applications.
One of the significant differences between single-phase power and three-phase power is the amount of power they can deliver. While three-phase power can deliver up to hundreds of kW, single-phase power is limited to a maximum capacity of around 10-20 kW. As such, it is ideal for smaller loads, such as residential appliances, lighting fixtures, and small motors.
Another critical aspect of single-phase power is the voltage level at which it is delivered. In the United States, single-phase power is typically delivered at either 120V or 240V, depending on the application. For instance, most residential outlets are rated for 120V, while larger appliances like ovens and dryers may require 240V.
Understanding the basics of single-phase power is essential for anyone who works with electrical systems or appliances regularly. Whether you’re an electrician or a homeowner, knowing how to use and maintain your electrical systems properly is critical. Therefore, learning about the ins and outs of single-phase power can help you make informed decisions about your electrical needs.
How to Convert 3-Phase Power to Single-Phase Power
Converting 3-phase power to single-phase power may sound like a complex task, but it’s actually quite achievable with the right equipment and knowledge. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different methods you can use to convert 3-phase power to single-phase power, including transformers, phase converters, and static converters.
The Magic of Transformers
Transformers are like magical devices that can change the voltage of an alternating current (AC) from one level to another. They’re great for applications that require a constant voltage output, such as powering a refrigerator or freezer. A transformer works by stepping down the voltage from the 3-phase input to the desired single-phase output voltage. For example, a transformer can be used to convert 220V 3-phase power to 120V single-phase power.
The Superhero Phase Converter
A phase converter is an electronic device that generates a third phase from the existing two phases to convert 3-phase power to single-phase power. This method is particularly useful for applications that require variable speed control, such as powering a drill press or lathe. There are two types of phase converters: rotary and static. Rotary phase converters use an induction motor to generate the third leg of power, while static phase converters use capacitors to create the third leg of power.
The Sidekick Static Converter
If you don’t need that much power, a static converter is a great option. This device uses capacitors and diodes to convert 3-phase power to single-phase power and is perfect for low power output needs, such as powering a small air compressor or fan.
Choosing the Right Method
When selecting a method for converting 3-phase power to single-phase power, it’s important to consider your specific needs. What voltage output do you need? How much power do you need? What type of load are you using? By answering these questions, you’ll be able to choose the best conversion method for your situation.
Conquer Your Electrical Needs
Converting 3-phase power to single-phase power may seem like a daunting task, but it doesn’t have to be. With the right equipment and planning, you can successfully convert 3-phase power to single-phase power and meet your electrical needs. So don’t be afraid to tackle this challenge and take control of your power supply.
Advantages of Converting 3-Phase to Single-Phase Power
Not only can it help save money on electricity bills, but it also offers greater flexibility in electrical equipment options.
One of the most significant advantages of converting to single-phase power is the potential cost savings associated with the conversion. Single-phase power is cheaper to install and maintain compared to 3-phase power, making it an appealing option for both businesses and homeowners. By reducing operating costs, converting to single-phase power can free up funds for other important investments.
Another advantage of converting to single-phase power is the increased availability of equipment. Most electrical equipment on the market is designed to run on single-phase power, meaning that businesses and homeowners who convert can access a wider range of equipment options. This translates to increased flexibility and more efficient use of resources.
In addition to greater flexibility in equipment options, converting to single-phase power also increases flexibility in the use of electrical appliances. Single-phase power allows for the use of smaller electrical devices, which are more flexible and easier to manage. This means that businesses and homeowners can use a wider range of electrical equipment without worrying about compatibility issues.
Furthermore, converting to single-phase power ensures a more consistent supply of electricity, reducing the risk of electrical disruptions and outages. This is especially important for businesses that rely heavily on technology and sensitive equipment. With a more stable supply of electricity, businesses can operate smoothly without any interruptions or costly downtime.
So, converting 3-phase power to single-phase power has several benefits that make it a valuable investment. It is cost-effective, increases equipment options, and allows for greater flexibility in the use of electrical appliances.
Disadvantages of Converting 3-Phase to Single-Phase Power
While it may seem like an attractive solution, it’s important to understand the potential disadvantages before making any decisions. As an expert in this field, I can tell you that there are several drawbacks to consider.
Firstly, converting a 3-phase system to a single-phase system can be costly. The additional equipment and labor required can make it an expensive process, which could be a significant barrier for many homeowners and businesses.
In addition to cost, there are also concerns around the efficiency of single-phase systems. Three-phase systems are designed to distribute power evenly across three separate phases, reducing power loss. However, single-phase systems only have one phase, resulting in an uneven distribution of power and leading to more power loss.
Furthermore, converting a 3-phase system to a single-phase system can result in reduced motor performance. Three-phase motors are designed to operate at specific frequencies and voltages, which can affect their horsepower and torque when converted to single-phase power. This can have a significant impact on the performance of your motors.
Lastly, safety concerns should not be overlooked when considering converting to single-phase power. Single-phase systems are more susceptible to voltage fluctuations and surges, which can damage equipment or even cause electrical fires if not managed properly.
In conclusion, while it may be possible to convert 3-phase power to single-phase power, it’s crucial to weigh the potential disadvantages against the benefits before making any decisions. The increased cost, efficiency concerns, reduced motor performance, and safety concerns should all be carefully considered before proceeding with any electrical system changes.
fCAs98_OS1E” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, converting from 3-phase to single-phase power may seem like a daunting task at first, but with the right tools and knowledge, it can be accomplished safely and efficiently. Understanding the fundamentals of electrical power and the differences between these two types of power is paramount in making informed decisions.
There are several methods for converting 3-phase power to single-phase power, including transformers, phase converters, and static converters. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed carefully before selecting the best one for your needs.
Switching to single-phase power offers numerous benefits such as cost savings, increased flexibility in equipment options, greater flexibility in appliance usage, and a more consistent supply of electricity. However, there are also potential drawbacks to consider like increased cost, efficiency concerns, reduced motor performance, and safety issues.
In summary, if you’re considering converting from three-phase to single-phase power for your home or business, it’s essential to evaluate all aspects thoroughly before making any decisions.