Have you ever heard of the incredible phenomenon known as cold welding?
It’s a process that defies traditional notions of how metal can be joined together. Imagine being able to fuse two pieces of metal together without the need for heat or an external agent – this is the magic of cold welding.
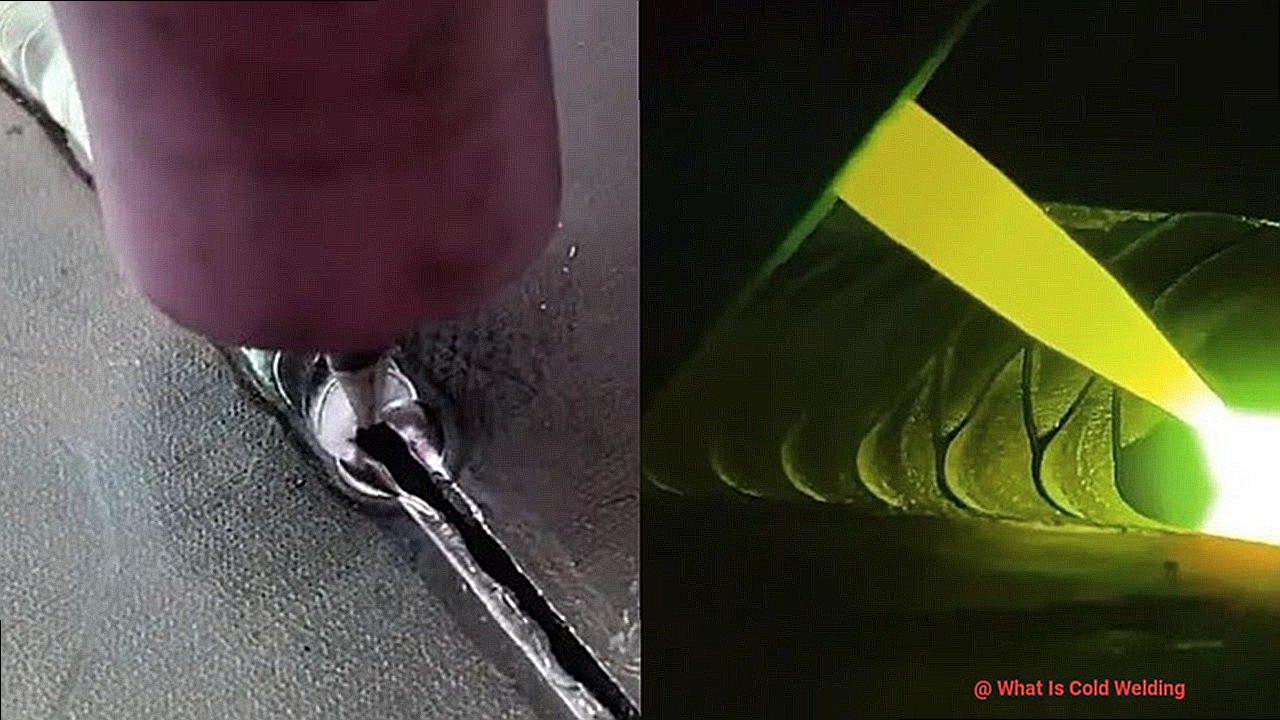

It might sound like something out of science fiction, but it’s a well-documented process that occurs naturally in outer space and has been successfully replicated in laboratories on Earth. The concept of cold welding can be mind-bending for those used to traditional welding methods involving high temperatures and filler metals.
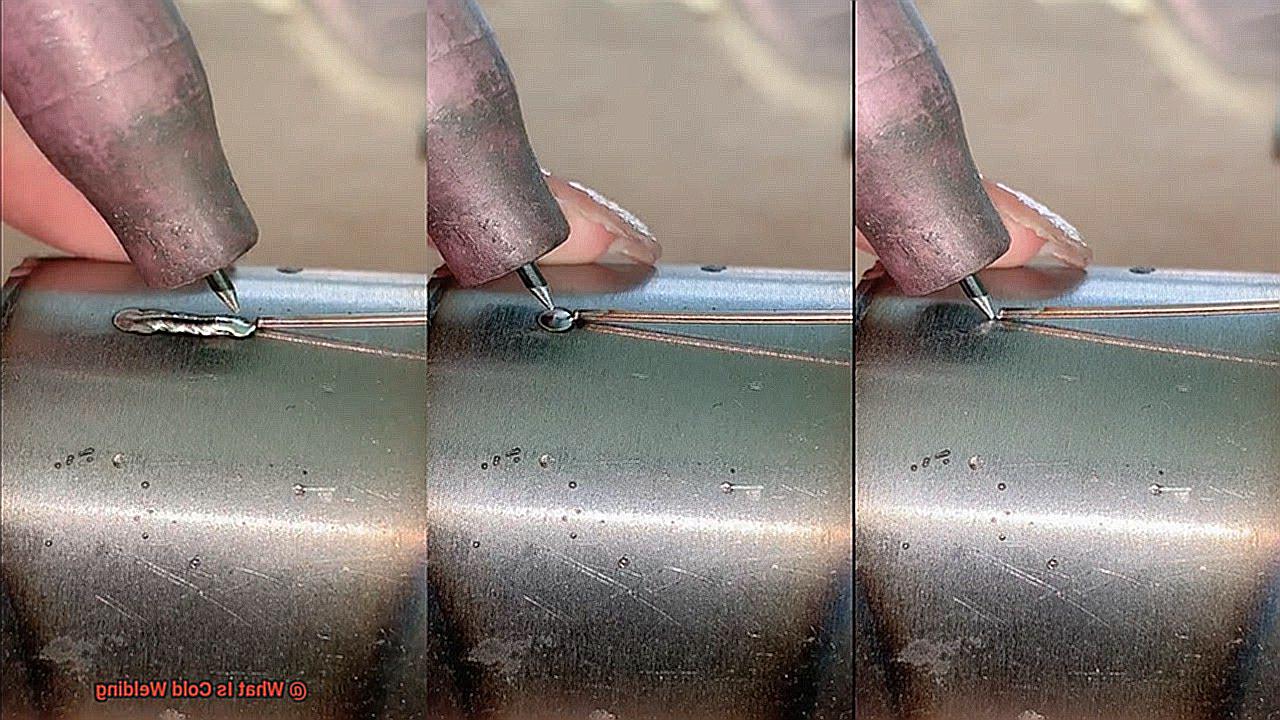
Cold welding, instead, relies solely on the intimate contact between two clean, flat metal surfaces. The contact generates a strong atomic bond due to the attraction between their atoms.

For years, scientists and engineers have been fascinated by this phenomenon and its potential applications are vast.
From space exploration to the manufacturing of high-tech electronics, cold welding could revolutionize the way we join metals together.
What is Cold Welding?
Contents
It may sound like a strange concept, but it’s known as cold welding – a fascinating process that has been used in various industries for decades.
The process of cold welding involves bringing two clean and flat metal surfaces into contact with each other under high pressure. This creates a molecular bond between the metals, which is incredibly strong and resilient.
The resulting joint is free from any distortion, warping or oxidation, making it ideal for applications where precision is crucial. This unique process offers many advantages, including the ability to join dissimilar metals without altering their properties.
This makes it an excellent option for applications where heat can cause damage to the metals or where different metals need to be joined together. Additionally, cold welding produces no harmful by-products such as fumes or gases, making it an environmentally friendly process.
However, there are some limitations to cold welding. It requires specific conditions such as a vacuum or inert gas environment to be effective, which may not be practical for all applications.
Furthermore, getting the metal surfaces clean enough for the process to work effectively can be challenging and time-consuming. Despite these limitations, cold welding remains a valuable technique for certain applications in various industries.
With proper cleaning and preparation, this fascinating process can produce strong and durable joints that are free from any distortion, warping or oxidation. It’s important to note that cold welding was first discovered in 1946 by the German physicist Fritz Heusler.
Since then, it has been used in various applications such as microelectronics, aerospace, and biomedical engineering. This process occurs due to the transfer of electrons between the two surfaces, which causes them to adhere to each other.
The absence of an oxide layer on the metal surfaces is essential to facilitate bonding. In conclusion, cold welding is a unique and effective process for joining two metal surfaces without using heat or additional materials.
History of Cold Welding
They used to produce gold wire by hammering gold nuggets, which brought two clean metal surfaces into contact with each other under high pressure.
This is essentially the same principle behind cold welding, a fascinating process that allows two metal surfaces to bond without using heat or additional materials. The scientific observation of cold welding did not occur until 1928, when the German physicist Johann Gottfried Tropsch noted that two clean metal surfaces would bond together when pressed against each other with sufficient force.
In 1941, two British scientists, P.G. Nuttall and R. M. Boseley, demonstrated the same effect by cold welding aluminum wires together.
They showed that the bond strength of the welded wires was comparable to that of the parent material, paving the way for the development of cold welding as a viable joining process for various metals. Thanks to its unique properties, cold welding quickly became a go-to process in various industries.
During the 1950s and 1960s, it was widely used in the aerospace industry for joining thin sheet metals used in spacecraft construction. It was also used in the production of electronic devices such as semiconductors, where it was essential to join small conductive wires without introducing any contaminants or heat.
Today, cold welding continues to be widely used in various industries for joining dissimilar metals and for creating hermetic seals. Its ability to join different materials without altering their properties and producing no harmful by-products makes it a star player in many manufacturing processes today.
In fact, it has become an essential tool for manufacturing microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which require precise and reliable bonding techniques.
So, while cold welding may have ancient roots, it has evolved into a valuable technique with a wide range of applications in modern industries such as aerospace and electronics.
Advantages of Cold Welding
As an expert in the field, I’m thrilled to share the many advantages of this unique process. First and foremost, cold welding doesn’t require any external heat or filler material to join two metal surfaces.
This makes it ideal for welding dissimilar metals that cannot be welded using traditional methods. And unlike other techniques, cold welding forms a bond at the atomic level, resulting in a metallurgically sound joint that’s stronger and more durable.
Another great thing about cold welding is that it’s a low-temperature process, which means there’s no risk of warping or distortion of the metal surfaces during the welding process. This feature makes it perfect for welding delicate or fragile components that can’t tolerate high temperatures.
Cold welding is also a clean and environmentally friendly process since it doesn’t produce any harmful fumes or gases.
This attribute makes it ideal for use in applications where safety and environmental concerns are critical. Finally, one of the best advantages of cold welding is just how fast and efficient it is.
Unlike traditional methods that require preheating, cooling, and post-treatments, cold welding can be completed quickly and efficiently, reducing production time and costs.
Limitations of Cold Welding
Although it is a fascinating method of joining metals without heat or electricity, it is not without its challenges.
One of the most significant limitations of cold welding is that it can only be used with certain metals. This process works best with metals that have a high ductility and surface cleanliness, such as gold, silver, copper, and aluminum.
If you’re working with other types of metals, cold welding might not be the best option for your project. In addition to this, achieving a precise fit between the two pieces of metal being joined is another challenge that comes with cold welding.
The surfaces must be perfectly clean and flat for the process to work effectively. This can prove to be difficult when working with larger or more complex pieces of metal.
So, it’s important to keep this in mind when deciding whether cold welding is suitable for your project. Furthermore, creating a strong bond between the two pieces of metal can also be a challenge with cold welding.
While it can create a bond that is almost as strong as a traditional weld, it may not be appropriate for applications where an extremely strong bond is required. Lastly, cold welding may not be suitable for applications where the joint will be subjected to extreme temperatures or pressure.
While cold welding can create a strong bond under normal conditions, it may not hold up under more extreme conditions. In conclusion, while cold welding is an excellent technique for joining certain types of metals, it does come with some limitations.
The Process of Cold Welding
It’s called cold welding, and it’s a fascinating process that utilizes pressure to bond two clean metal surfaces together.

This method, also known as solid-state welding, is made possible through the phenomenon of cold welding, where metallic bonds are formed between the atoms at the interface of the two surfaces. The pressure required for cold welding is relatively high, ranging from a few hundred to several thousand pounds per square inch.
However, this pressure can be achieved without the need for high temperatures, making it an excellent option for joining metals that cannot withstand heat. Cold welding has proven to be especially useful in industries such as aerospace and medicine.

In the aerospace industry, it’s used to join small parts together that are difficult to weld using traditional methods. Meanwhile, in the medical industry, it’s used to join small components in implantable medical devices.
Although cold welding is an efficient method for joining metals, there are a few factors that can affect its success. Surface contamination is one such factor that can prevent proper bonding between the metals.
To ensure successful bonding, it’s crucial to clean and remove any oils or other contaminants before attempting cold welding. Surface roughness is another factor that can impact its effectiveness; surfaces that are too smooth can make it difficult for the atoms to diffuse and form bonds.
V7-mcjR59a4″ >
Applications of Cold Welding
Cold welding is a remarkable process that has revolutionized several industries, providing a cost-effective and efficient way to join different metals together.
This technique involves applying pressure to two metal surfaces without using heat or adhesives, resulting in a strong bond that is ideal for many applications. Let’s explore some of the fascinating ways cold welding is used in different industries.
The aerospace industry relies heavily on cold welding to manufacture components such as fuel tanks, hydraulic lines, and electrical connectors. The process is perfect for joining different materials like aluminum, titanium, and other alloys, creating strong bonds that can withstand the harsh conditions of space travel.
In the electronics industry, cold welding is used to create electrical contacts without soldering. This method creates a robust bond between two metal surfaces without any heat or additional materials.
It is widely used in the manufacturing of microelectronic components like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits. The medical industry also uses cold welding to create precise medical devices like surgical instruments, dental implants, and prosthetics.
Cold welding helps in joining two or more metals without using any permanent adhesives or heat sources, ensuring the devices are both safe and effective. In the automotive industry, cold welding plays a critical role in producing lightweight vehicles.
By joining different metals together without adding any extra weight, it helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, increasing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Finally, cold welding is also utilized in the jewelry industry to create intricate designs and patterns on jewelry pieces.
Jewelers can join different metals together without using any heat or adhesives, allowing them to create stunning pieces that are both durable and visually appealing. In conclusion, cold welding is a versatile method for joining different metals together without using heat or adhesives.

Also Read: How to repair wrought iron without welding? – The Welding Guru
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold welding is a truly remarkable process that challenges conventional notions of metal joining.
By applying pressure to two clean and flat metal surfaces without the use of heat or adhesives, cold welding creates a bond that is both strong and versatile. It’s no wonder that this concept may seem like something out of science fiction, but it’s a well-documented process that has been successfully replicated in laboratories on Earth and occurs naturally in outer space.
One of the most significant advantages of cold welding is its ability to join dissimilar metals without altering their properties. Heat can often damage metals or change their composition, making traditional welding methods unsuitable for certain applications.
Cold welding offers an excellent solution to these problems by producing no harmful by-products such as fumes or gases, which makes it environmentally friendly. Although there are some limitations to cold welding, such as its requirement for specific conditions and surface cleanliness, its potential applications are vast.
From space exploration to the manufacturing of high-tech electronics, cold welding could revolutionize the way we join metals together. Overall, the power of cold welding continues to amaze scientists and engineers alike.
Its unique properties make it a valuable technique for certain applications in various industries today and will undoubtedly continue to do so in the future.





