Welding is a complex and challenging task that demands skill, focus, and safety precautions. One of the most critical safety measures in welding is protecting your eyes from the intense light and radiation generated during the process. This is where welding shade numbers come into play – they determine how much light your eyes are exposed to while you’re welding.
As a welder, you’ve probably heard about welding shade numbers, but do you know what they mean? How do they impact your safety while welding, and how can you choose the right shade number for your specific project? In this blog post, we’ll answer these questions and provide you with a comprehensive guide on everything you need to know about welding shade numbers.
From understanding the basics of welding shade numbers to selecting the optimal shade for your project, our guide has got you covered. With this knowledge at hand, you can protect your vision and take your welding skills to new heights. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced welder, this post is an essential read for anyone who values safety and wants to achieve exceptional results in their work.
So let’s jump into the world of welding shade numbers together. By the end of this post, you’ll have all the information you need to make informed decisions about protecting yourself while welding.
a. Definition of Welding Shade Numbers
Contents
- 1 a. Definition of Welding Shade Numbers
- 2 What Are Welding Shade Numbers and Why Are They Important?
- 3 How Do Shade Numbers Work?
- 4 Benefits of Appropriate Shade Number Selection
- 5 Different Types of Welding and Their Recommended Shade Numbers
- 6 Dangers of Using the Wrong Shade Number
- 7 How to Choose the Right Shade Number for Your Job
- 8 Tips for Safely Wearing and Operating a Welding Helmet
- 9 Conclusion
Welding is a craft that requires a steady hand, quick reflexes and a keen eye. But when it comes to the eyes, welding can be particularly dangerous. This is where welding shade numbers come in. Welding shade numbers are a system used to indicate the level of protection required for the eyes and face during welding. They help determine the appropriate shade of lens filter needed to protect a welder’s eyes from harmful radiation and intense light emitted during the welding process.
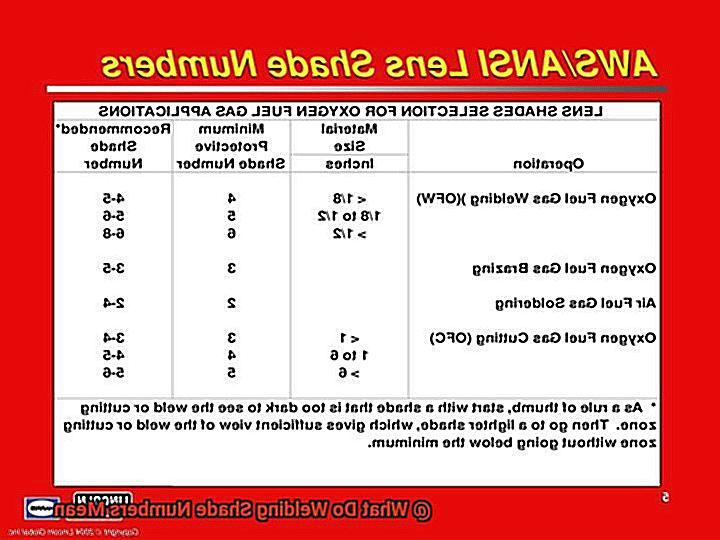
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has established a standard for welding shade numbers, which ranges from 1 to 1The higher the number, the darker the shade of lens filter required. Shade 1 is the lightest, while shade 14 is the darkest.
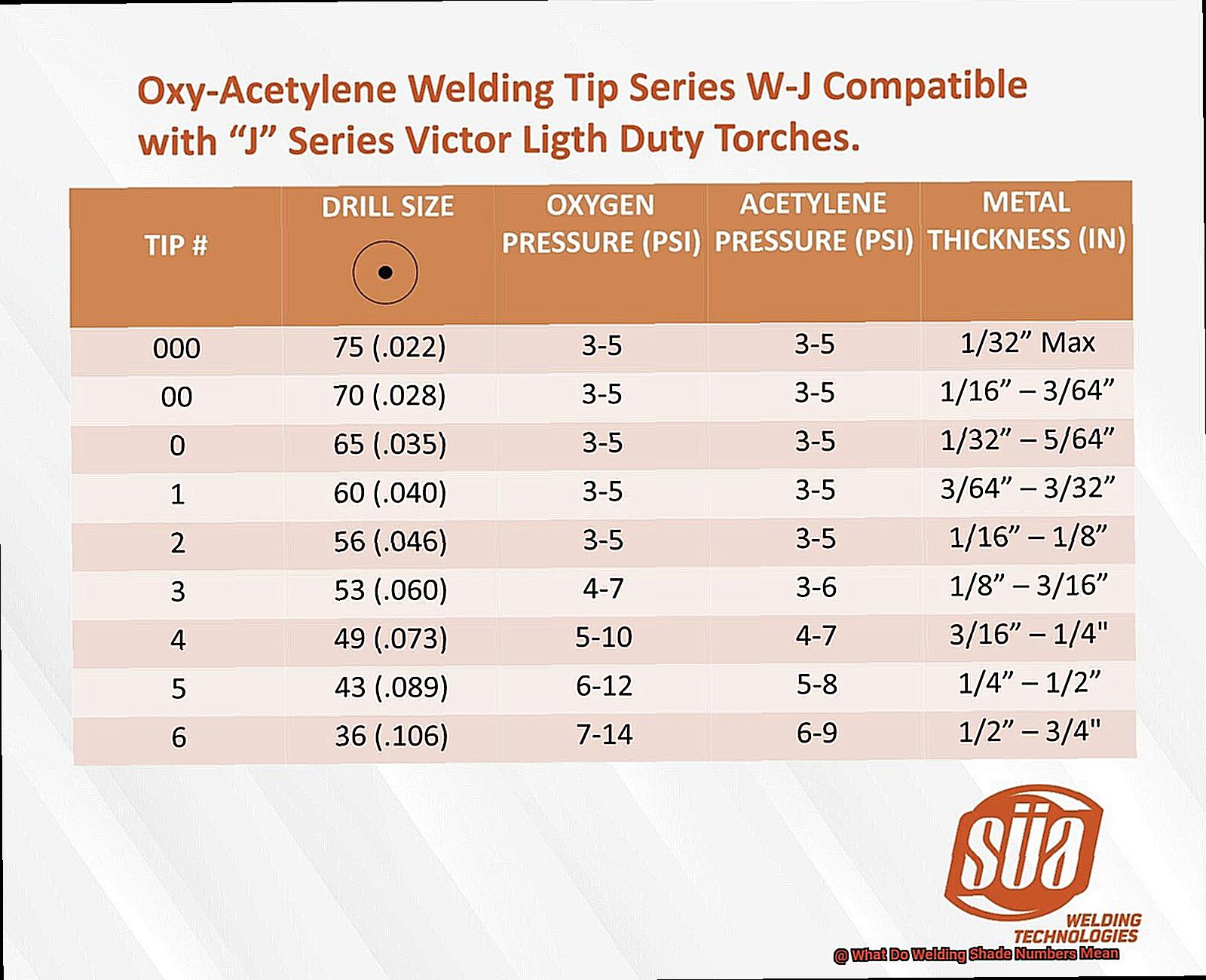
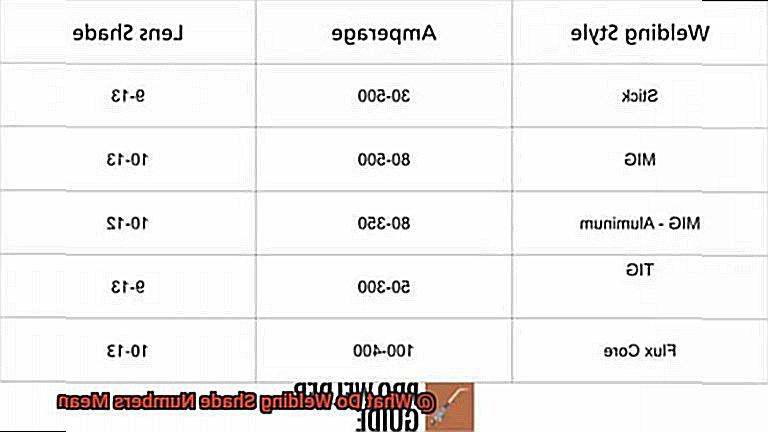
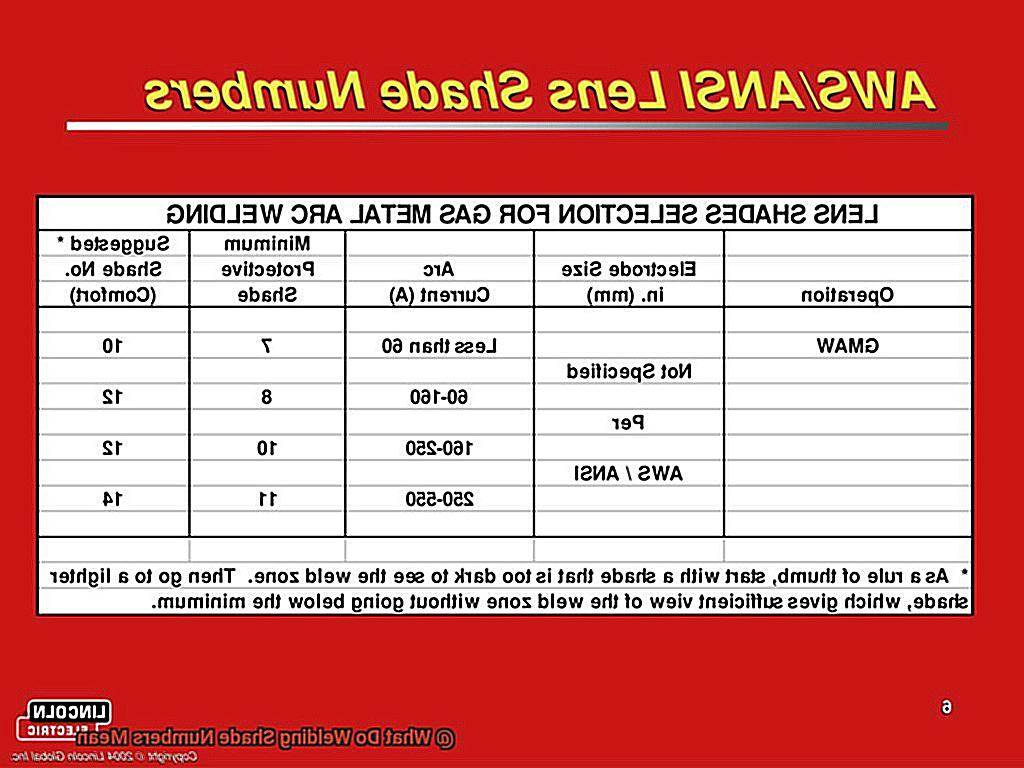
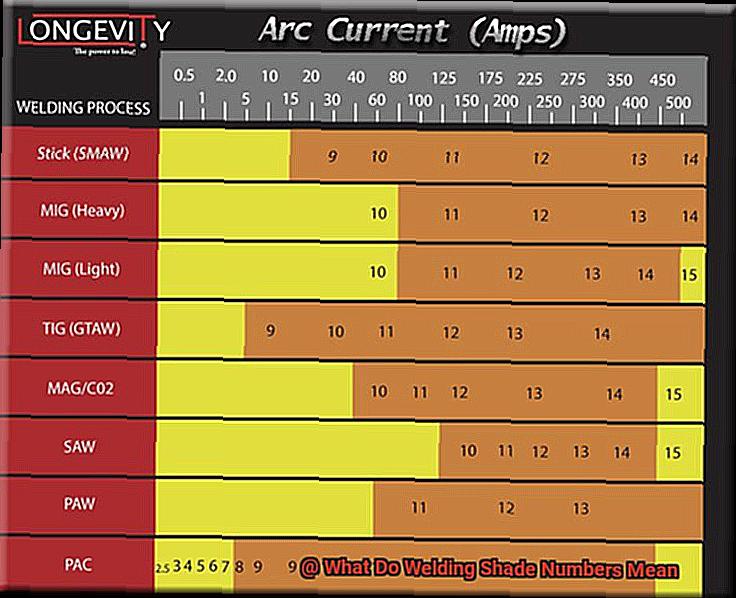
Different types of welding require different levels of shade protection. For example, gas welding typically requires a shade number of 4, while stick welding may require a shade number of 9-13 depending on the amperage used. TIG welding, on the other hand, typically requires a shade number between 8 and 13, while MIG welding may require a shade number between 10 and 14.
It is important for welders to use the appropriate shade number for their specific welding application to ensure optimal safety and protection. Using a shade that is too light can result in eye damage and blindness, while using a shade that is too dark can make it difficult to see the weld pool and result in poor quality welds.
To put it simply: Welding shade numbers are essential for protecting your eyes while welding. By using a helmet with an appropriate shade number, you can ensure your safety by preventing eye damage or blindness. Additionally, using an appropriate shade number will allow you to see what you are working on clearly, resulting in high-quality welds.
So always make sure to follow ANSI standards when selecting your welding helmet and use the appropriate shade number for each specific welding process.
What Are Welding Shade Numbers and Why Are They Important?
These numbers indicate the level of darkness or shade that a helmet or lens provides, which is essential in safeguarding the welder’s eyes from the intense light generated during the welding process. It’s no secret that welding can be a dangerous job; however, ensuring you have the appropriate shade number can make all the difference between a successful weld and a potential disaster.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) set standards for welding shade numbers based on various factors, such as the type of welding process and amperage used. For example, shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), also known as stick welding, typically requires a shade number of 10-14, while gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding, may only require a shade number of 8-13.
It’s important to note that using a shade number that is too light can result in eye damage, while using a shade number that is too dark can make it difficult to see the weld area, increasing the risk of accidents. Therefore, it is crucial for welders to understand the recommended shade numbers for their specific welding applications and ensure they use helmets or lenses that provide adequate protection.
How Do Shade Numbers Work?
As a welder, you know how important it is to protect your eyes from the intense light and sparks generated during welding. But do you know how welding shade numbers work and how to choose the appropriate shade number? Let’s explore.
Welding shade numbers indicate the level of protection provided by a lens or filter against harmful rays emitted during welding. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have established safety standards for welding, which include using appropriate shade numbers for each type of welding.
The welding shade number is determined by the amount of light that passes through the lens or filter. The higher the shade number, the darker the lens or filter, which means less light passes through. For example, a shade 3 lens allows more light to pass through than a shade 10 lens.
Choosing the right shade number depends on several factors such as the type of welding being performed, the welding method, and the welding current intensity. It’s crucial to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or OSHA guidelines to determine the appropriate shade number for your specific welding application.
It’s important to note that using a lens or filter with a shade number that is too low can result in eye damage from exposure to harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation. On the other hand, a lens or filter with a higher shade number than recommended can make it difficult for you to see your workpiece clearly, leading to poor quality welds and potential safety hazards.
Benefits of Appropriate Shade Number Selection
As a welder, you know that your eyes are one of your most valuable tools. That’s why selecting the right shade number for your welding helmet is essential for both safety and quality of work. But what makes appropriate shade number selection so important? Let’s explore the benefits.
First and foremost, selecting the right shade number reduces eye strain and fatigue. Welding can be a time-consuming activity, and staring at a bright light for hours on end can take a toll on your eyes. By choosing the appropriate shade number for your helmet, you can reduce eye strain and fatigue, allowing you to work more efficiently and safely.
But that’s not all- selecting the correct shade number also protects your eyes from harmful UV and IR radiation produced during welding. These harmful rays can cause severe eye damage if not protected against. By filtering out these harmful rays with the right shade number, you can ensure that your eyes are safe from long-term damage.
In addition to protecting your eyes from harm, choosing the right shade number ensures clear visibility of your work. Using a shade that is too dark can make it difficult to see what you’re working on, leading to mistakes and potentially dangerous situations. On the other hand, using a shade that is too light can cause eye strain and fatigue, making it challenging to focus on your work. By selecting the appropriate shade number, you can avoid these issues and work more effectively.
Overall, appropriate shade number selection is like putting on armor to protect yourself in battle. It reduces eye strain and fatigue, filters out harmful radiation, and ensures clear visibility of your work.
Different Types of Welding and Their Recommended Shade Numbers
This is where welding shade numbers come in. These numbers represent the darkness level of the filter lens in a welding helmet, with higher numbers indicating darker lenses.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) and Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) require shade numbers 10-12 for optimal protection. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) requires a slightly darker lens with a recommended shade number of 12-1Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), also known as stick welding, requires the darkest shade number with a recommendation of 14-16.
However, these recommendations are just guidelines and may need to be adjusted based on factors such as the welding amperage and the metal being welded. It’s important to consider these variables when selecting the appropriate shade number for your welding helmet.
But choosing the right shade number isn’t the only consideration. A high-quality welding helmet is equally important for maximum protection and comfort. Features such as reliable auto-darkening and durable construction provide additional peace of mind for the welder.
In conclusion, understanding the recommended shade numbers for different types of welding is essential for protecting your eyes during each job. So, make sure you choose a high-quality welding helmet with the appropriate shade number to ensure safe and efficient welding.
TIG Welding
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, it’s important to understand why selecting the correct shade number for your welding helmet is crucial for this process.
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular welding technique for welding thin sections of stainless steel, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals. However, what many people don’t realize is that TIG welding produces higher levels of UV radiation than other welding methods.
That’s where the shade number of your welding helmet lens comes in. The shade number represents the darkness of the lens and protects your eyes from harmful radiation produced during welding. For TIG welding, a darker shade number is required compared to other processes to provide adequate protection.
For TIG welding, it’s recommended to use a shade number between 8 and 1However, a shade number of 10 is commonly used in most applications. This shade number provides enough protection against harmful radiation while still allowing you to see the weld puddle clearly.
But don’t forget: the shade number required for TIG welding may vary depending on the material being welded and the amperage used. As amperage increases, so does the necessary shade number to ensure proper eye protection.
Protecting your eyes during TIG welding isn’t just about selecting the right shade number for your helmet. Make sure you’re using high-quality equipment with reliable auto-darkening and durable construction. This will ensure safe and efficient TIG welding every time.
MIG Welding
MIG welding is a popular welding process that uses a spool of wire feeding through a gun to create an electric arc between the wire and the workpiece. This produces heat, which melts both the wire and workpiece, causing them to fuse together. But how do you determine the right shade number for your welding helmet? Well, it’s not as complicated as it may seem.
For MIG welding, you’ll need to use a specific level of protection. Typically, MIG welding requires a shade level of 10-1However, the specific shade number needed will depend on the amperage used for the welding process. For example, lower amperage levels will require a lower shade level while higher amperage levels will require a higher shade level.
To determine the correct shade number for your MIG welding project, start by checking the amperage level you’ll be using for your weld. If you’re unsure about this, don’t hesitate to consult with an expert or refer to your welder’s manual.
Once you know your amperage level, consult with the manufacturer’s recommended shade chart to determine the appropriate shade range for your project. As mentioned earlier, you’ll typically need a shade level of 10-13 for MIG welding.
It’s crucial to use the correct shade number to protect your eyes from harmful UV and IR radiation. Using a shade number that is too low can damage your eyesight permanently. Conversely, using a shade number that is too high may make it difficult for you to see what you’re working on clearly enough.
Stick Welding
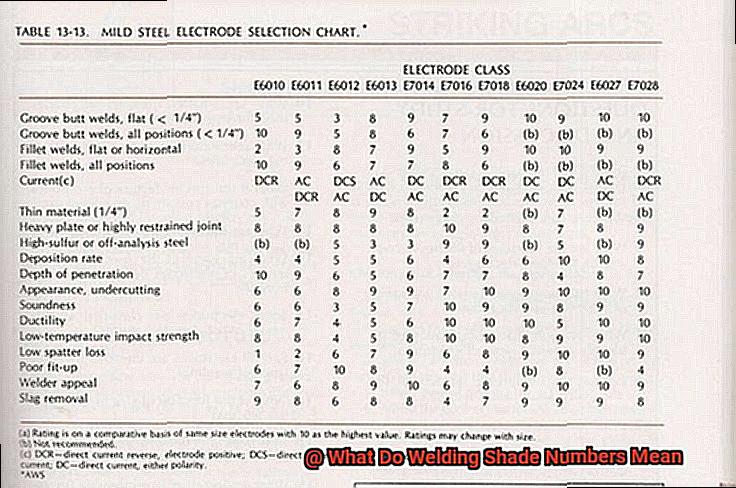
Stick welding, also known as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), is a powerful and widely used welding technique that requires precision, skill, and the right equipment. One essential piece of protective gear for stick welding is a welding helmet with the appropriate shade number.
The shade number of the helmet lens is critical as it determines the level of protection against harmful UV and IR radiation emitted during the welding process. A higher shade number means a darker lens and more protection.
For stick welding, a shade number between 9 and 13 is recommended. A shade 9 lens provides adequate protection for low amperage welding, while a shade 13 lens is suitable for high amperage welding. However, the exact shade number required may vary depending on factors such as electrode type, amperage settings, and ambient lighting conditions.
It’s crucial to use a helmet with the correct shade number to protect your eyes from prolonged exposure to UV and IR radiation. If you use a lens with a lower shade number than recommended, it can lead to eye damage. Similarly, if you use a lens with a higher shade number than necessary, it can make it challenging to see the welding area clearly, leading to mistakes and accidents.
In conclusion, stick welding may seem like a simple process, but it requires careful attention to detail and proper safety precautions. Using a welding helmet with the appropriate shade number is an essential step to ensure eye safety and accurate welding results.
Dangers of Using the Wrong Shade Number
As a welder, you know the power of welding and the importance of using the right equipment to protect yourself from harmful radiation. But did you know that using the wrong shade number can be dangerous? Welding shades range from 1 to 14, with 1 being the lightest and 14 being the darkest. The shade number you choose depends on factors such as electrode type, amperage settings, and ambient lighting conditions.
Using a shade that is too light may seem like a minor inconvenience, but it can cause serious problems. Eye strain, fatigue, headaches, and decreased productivity are just a few of the issues that can arise. Long-term damage to the eyes, such as cataracts and retinal burns, is also a risk. Don’t let short-term gains lead to long-term pain.
On the other hand, using a shade that is too dark can be just as dangerous. It makes it difficult to see the workpiece clearly, which can lead to mistakes and potential hazards. Accidents caused by impaired vision can be severe and life-threatening. Don’t let darkness cloud your judgment and put yourself in danger.
So how do you choose the right shade number for your welding process? The American Welding Society provides guidelines on recommended shades for different processes and amperage levels. However, it’s important to consider all factors when selecting your shade number. Arc length, electrode size, distance from the workpiece, and helmet condition are all critical factors to take into account. Don’t overlook any detail that could impact your safety and performance.
In addition to using the correct shade number, maintaining your helmet is also essential. A damaged or improperly maintained helmet can compromise the protection provided by the shade number. Don’t let wear and tear weaken your defense against harmful radiation.
Choosing the correct shade number is crucial for both safety and productivity. Don’t risk your eyesight or your livelihood by using the wrong shade number. Take the time to select the right one for your welding process and follow recommended guidelines. Your eyes will thank you in the long run.
How to Choose the Right Shade Number for Your Job
Welding can be an exhilarating and worthwhile career choice, but it’s also a hazardous one. That’s why selecting the right shade number for your welding helmet is critical to protecting your eyes from harmful rays.
It’s like choosing sunglasses for a bright, sunny day – you want to shield your eyes from harm, but you also want to have a clear view of what’s in front of you.
To help you choose the perfect shade number for your welding job, let’s consider five crucial factors:
Welding process
Different welding processes emit varying levels of brightness, which means they require different shade numbers. TIG welding typically requires a lower shade number than stick welding because it produces less brightness.
Material thickness
Thicker materials demand higher shade numbers because they emit more brightness. It’s essential not to risk damaging your eyes by using a shade number that’s too low.
Amperage setting
Higher amperage settings produce more brightness, so they also require higher shade numbers.
Personal comfort
While it’s crucial to choose a shade number that provides adequate protection, you also want to make sure you can see what you’re working on clearly. Some welders prefer a slightly lighter or darker shade than what is recommended based on their specific job requirements.
Additional hazards
If there are any additional hazards present, such as overhead hazards or confined spaces, they may require a higher shade number for maximum protection.
Tips for Safely Wearing and Operating a Welding Helmet
Welding is a fascinating process that requires skill, precision, and most importantly, safety. As a welder, you must take necessary precautions to protect yourself from the harmful radiations, flying debris, and sparks that come with the job. One of the most critical pieces of equipment in welding is a welding helmet. However, it’s not enough to just wear a welding helmet; you need to wear it safely. Here are some tips for safely wearing and operating a welding helmet.
Ensure Proper Fit
The first thing to consider when wearing a welding helmet is its fit. The helmet should fit snugly on your head to ensure maximum protection. However, it shouldn’t be too tight as this can cause discomfort and headaches. If it’s too loose, it won’t provide enough protection from the harmful radiations.
Choose the Appropriate Shade Number

The shade number of your welding helmet is crucial to your safety. It determines the darkness of the lens and protects your eyes from harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays. The shade number you choose will depend on the type of welding you are doing, the amperage, and the material you are working with. Generally, a shade number between 10 and 13 is recommended for most welding applications.
Check the Lens Regularly
Another important aspect of wearing a welding helmet safely is checking the lens regularly for scratches or damage. A scratched lens can reduce its effectiveness and expose you to harmful radiations. Check your lens before every use and replace it if necessary.
Keep Your Helmet Clean
A dirty welding helmet can obstruct your vision and compromise your safety. Regularly clean the lens and the inside of your helmet with a soft cloth or sponge. Avoid using abrasive materials or solvents that can scratch or damage the lens.
Store Your Helmet Properly
When not in use, store your welding helmet in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Exposure to sunlight and heat can damage the helmet’s lens, reducing its effectiveness.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you are using your welding helmet safely and protecting yourself from harm. Remember, safety should always be your top priority when welding.
c1VMKv5YQe4″ >
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding welding shade numbers is essential for welders to protect their eyes and ensure a successful welding project.
The shade number indicates the level of darkness in the welding lens, with higher numbers providing more protection from intense light. It’s crucial to choose the appropriate shade number based on the type of welding and amperage used.
With this knowledge, welders can confidently tackle any welding job while keeping their eyes safe and protected.